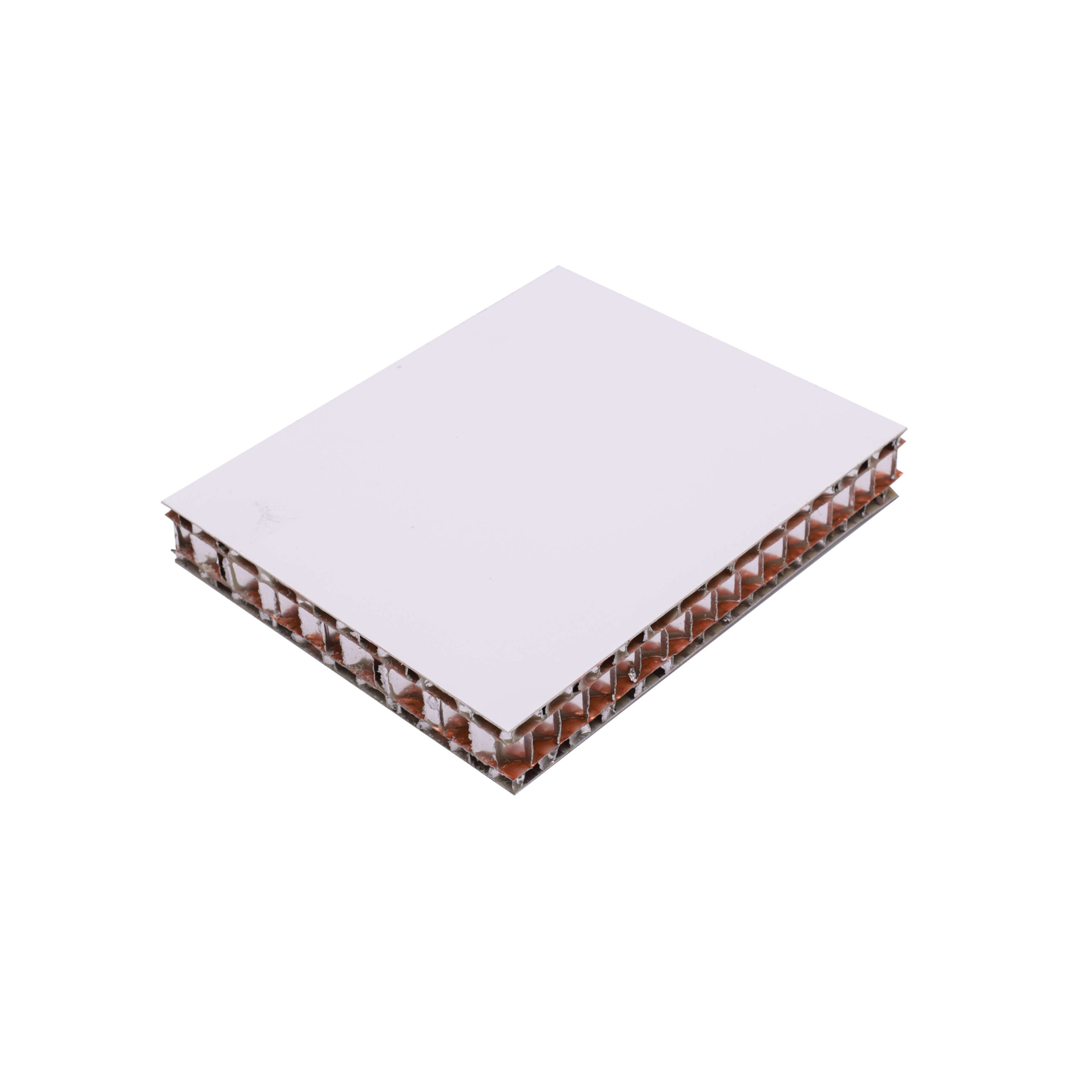
As a kind of lightweight high-temperature composite material, honeycomb board has emerged in recent years in the fields of architecture, interior design and many industrial fields. Its unique structure and excellent performance make it the preferred material for designers and engineers. This article will introduce you to the characteristics, applications, and importance of honeycomb panels in modern design.
Basic characteristics of honeycomb board
Honeycomb board is a composite material made of two thin panels bonded together with a honeycomb core in the middle. This honeycomb structure mimics the design of a bee’s nest and is known for its efficient mechanical properties and lightweight characteristics. Here are the main features of honeycomb panels: 1. Lightweight and high strength: Honeycomb panels are lightweight, but they have extremely high compressive and bending strength, making them excel in applications where high strength is required but weight is limited.
- Sound insulation and heat insulation: The large number of closed spaces inside the honeycomb structure gives the material good sound insulation and heat insulation performance, suitable for places with high requirements for sound and heat environment.
- Environmentally friendly and sustainable: The honeycomb board can use recycled materials in the production process, and there is little waste, which conforms to the concept of modern environmental protection and sustainable development.
- Easy to process: honeycomb board can be cut, bent and formed according to design requirements, flexible processing, suitable for all kinds of complex designs.
- Application fields of honeycomb board
Due to its unique performance, honeycomb board has been widely used in many fields: - Building curtain wall: honeycomb board is often used in the exterior decoration of buildings. It is not only beautiful and elegant, but also can provide good sound insulation and heat insulation effect, and improve the overall energy efficiency of buildings.
- Interior decoration: In interior design, honeycomb board can be used for walls, ceilings and partitions. Its flat surface and diverse color options make it an ideal material for improving the quality of space.
- Transportation: The lightweight and high-strength characteristics of honeycomb panels make them popular in the interior manufacturing of vehicles, trains, and airplanes, helping to reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency.
- Furniture manufacturing: honeycomb panels can be used to make various types of furniture, such as tables and cabinets, and their high strength and stability ensure the durability and aesthetics of furniture.
- The importance of honeycomb panels in modern design
In modern design, honeycomb board is not only a functional material, but also a fashionable design element. Its simple lines and diverse surface treatment effects can meet the needs of different design styles. Here are several prominent advantages of honeycomb board in modern design. - Innovative design: The structural characteristics of honeycomb panels provide designers with greater creative freedom, enabling them to achieve design effects that are difficult to achieve with traditional materials.
- Sustainable development: With the increasing awareness of environmental protection, the sustainable and environmental characteristics of honeycomb board make it a choice in line with the trend of the times.
- Economical and efficient: The honeycomb board not only has superior performance, but also can reduce maintenance costs in long-term use, and has high economic benefits.
4. Conclusion
With its unique performance and diverse applications, honeycomb board is changing our traditional perception of architecture and design. Whether in building curtain walls, interior decoration, or transportation and furniture manufacturing, honeycomb board has shown great potential. In the future, with the continuous progress and innovation of technology, cellular board will play an important role in more fields and become an indispensable part of modern design and architecture.